Imagine a world where students are no longer bound by the limitations of traditional classroom settings. Where technology becomes an integral part of their learning experience, pushing the boundaries of education as we know it. Enter “The Future of Education: Embracing Technological Innovation,” a groundbreaking product that promises to revolutionize the way we teach and learn. With its innovative features and cutting-edge advancements, this product aims to bridge the gap between students and technology, enhancing their academic journey and preparing them for a rapidly evolving digital world. Get ready to step into the future of education, where limitless possibilities await.
The Impact of Technological Innovation on Education
1.1 Enhanced Access to Education
Technological innovation has greatly enhanced access to education, breaking down barriers and expanding opportunities for learners around the world. Through online platforms, learners can access educational resources, courses, and expertise that may not have been available to them otherwise. Whether it’s through online learning platforms or massive open online courses (MOOCs), individuals can now pursue education at their own pace and convenience, regardless of their location or socioeconomic background. This accessibility has opened doors for lifelong learning and bridging the educational divide.
1.2 Personalized Learning Experience
With the help of technology, education has shifted towards a more personalized learning experience. Adaptive learning systems powered by artificial intelligence (AI) can analyze individual student data and tailor instruction to meet their specific needs. Students can learn at their own pace, focusing on areas where they need more support and progressing faster through topics they have already mastered. This personalized approach not only enhances students’ understanding and retention of concepts but also boosts their motivation and engagement with the learning process.
1.3 Improved Collaboration and Communication
Technology has revolutionized collaboration and communication in education. Through online platforms, students can easily connect and collaborate with their peers, irrespective of geographical barriers. Online forums, chat rooms, and video conferencing tools facilitate seamless communication and enable students to engage in virtual group projects, discussions, and debates. This not only enhances their social and communication skills but also fosters a sense of community and creates a global learning environment where diverse perspectives can be exchanged.
1.4 Enriched Learning Resources
Technological innovation has resulted in a wealth of learning resources that go beyond traditional textbooks. Digital textbooks, interactive multimedia content, educational apps, and online libraries offer students a wide range of resources to enhance their learning experience. These resources often incorporate visuals, simulations, and interactive elements that make complex concepts more engaging and easier to grasp. Additionally, educational platforms provide access to a vast repository of educational videos, podcasts, articles, and research papers, empowering students to explore their interests and deepen their understanding of various subjects.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Education
2.1 Adaptive Learning with AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies play a significant role in the integration of technology in education. Adaptive learning systems powered by AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of student data, identify patterns, and provide personalized learning pathways for each student. These systems continuously adapt and adjust the content and pace of instruction based on individual student progress, ensuring that learning is tailored to their specific needs. This adaptive learning approach optimizes students’ learning outcomes and maximizes the efficient use of educational resources.
2.2 Intelligent Tutoring Systems
Intelligent tutoring systems leverage AI to provide individualized support and guidance to students. These systems can assess students’ knowledge, skills, and learning gaps, and provide targeted feedback and recommendations. They simulate one-on-one tutoring interactions, offering personalized instruction and adapting their approach based on the student’s responses. Intelligent tutoring systems not only enhance students’ understanding of the subject matter but also foster metacognitive skills and encourage self-regulated learning.
2.3 AI-powered Grading and Assessment
AI technology has also transformed the grading and assessment processes in education. With the help of AI algorithms, grading can be automated, saving educators significant time and effort. AI-powered assessment tools can analyze and evaluate student responses, providing instant feedback and generating detailed reports on students’ performance. This real-time feedback allows students to identify areas of improvement and educators to adapt their teaching strategies accordingly, leading to more effective learning outcomes.
2.4 Virtual Assistants for Students
Virtual assistants, driven by AI, have the potential to assist students in their learning journey. These virtual assistants can answer students’ questions, provide explanations, offer study tips, and even engage in interactive dialogue to facilitate comprehension. By having access to virtual assistants anytime and anywhere, students can receive immediate support, reducing frustration and enhancing the learning process. Virtual assistants can also aid students with organizing their study schedules, setting reminders, and managing their academic tasks, promoting better time management and productivity.

This image is property of cdn.elearningindustry.com.
Gamification in Education
3.1 Engaging Learning Experience
Gamification involves the integration of game-like elements into the learning process to enhance engagement and motivation. By adding elements such as challenges, rewards, leaderboards, and levels, education becomes more interactive and enjoyable for students. Gamified learning experiences create a sense of achievement and progress, encouraging students to persist in their learning journey and overcome challenges. This increased engagement boosts retention and deepens understanding of concepts.
3.2 Motivating Performance and Progress
Gamification in education provides students with immediate feedback and recognition for their achievements, fostering a sense of accomplishment and motivation. By earning badges, leveling up, or unlocking virtual rewards, students feel a sense of progress and are motivated to continue learning. This gamified approach taps into intrinsic motivation, making the learning process more enjoyable and increasing students’ willingness to invest their time and effort into learning.
3.3 Enhancing Problem-solving Skills
Games often require players to solve problems and make decisions in dynamic and complex environments. By incorporating gaming elements into educational activities, students can develop and enhance their problem-solving skills. Gamified learning environments encourage critical thinking, strategic planning, and creativity as students navigate through challenges and puzzles. These problem-solving skills are transferable to real-life situations, equipping students with valuable skills for their future endeavors.
3.4 Leverage of Game-based Assessments
Gamification extends to assessments, where game-based assessments offer an interactive and immersive alternative to traditional exams and quizzes. Through game-based assessments, students can demonstrate their knowledge and skills in a more engaging and authentic manner. These assessments often involve scenarios, simulations, and interactive tasks, providing a more comprehensive and holistic evaluation of students’ abilities. Game-based assessments promote active learning and provide educators with valuable insights into students’ competencies and areas for improvement.
Virtual and Augmented Reality in Education
4.1 Immersive Learning Environments
Virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) technologies create immersive learning environments that transport students into virtual worlds or overlay digital information onto the real world. These immersive experiences allow students to visualize and interact with complex concepts, enhancing their understanding and retention. For example, in science classes, students can explore the human body or conduct virtual experiments, providing a hands-on and interactive learning experience.
4.2 Virtual Field Trips
Virtual reality enables students to embark on virtual field trips to places that may be geographically distant or inaccessible. Through VR headsets or immersive VR experiences, students can visit historical sites, explore different cultures, or even venture into outer space. Virtual field trips supplement traditional classroom learning by providing students with firsthand experiences and expanding their worldview.
4.3 Simulation-based Learning
Augmented reality and virtual reality offer simulation-based learning, where students can practice and apply their knowledge and skills in realistic scenarios. For example, medical students can perform virtual surgeries, engineering students can design and test prototypes, and language learners can engage in immersive language conversations. This hands-on approach enhances students’ practical skills and allows them to learn from mistakes without real-world consequences.
4.4 Enhanced Visualization of Complex Concepts
Virtual and augmented reality technologies enable the visualization of abstract or complex concepts that might be challenging to understand through traditional methods. By visualizing scientific models, mathematical equations, or spatial relationships, students can develop a deeper understanding of these concepts. The immersive nature of VR/AR engages multiple senses, facilitating cognitive processes and improving conceptual understanding.

This image is property of www.besonline.in.
Internet of Things (IoT) in the Classroom
5.1 Smart Classroom Management
The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed traditional classrooms into smart classrooms. IoT devices, such as smart boards, cameras, sensors, and wearables, enable educators to manage classrooms effectively. Smart boards provide interactive and dynamic teaching tools, enhancing student engagement and participation. Cameras and sensors can monitor classroom activities, detect student behavior patterns, and provide valuable insights for educators to optimize their teaching practices.
5.2 Real-time Monitoring and Tracking
IoT devices in the classroom facilitate real-time monitoring and tracking of student progress and performance. Wearable devices or sensors can collect and analyze data on students’ attendance, participation, and engagement levels. Educators can track these data points to identify students who may need additional support or intervention and tailor their instruction accordingly. Real-time tracking also allows educators to provide timely feedback and address students’ needs promptly.
5.3 Enhanced Safety and Security
IoT devices enhance safety and security measures in the classroom. Through IoT-enabled surveillance systems, schools can monitor and identify potential security threats. Smart locks and access control systems further enhance physical security by restricting unauthorized access. IoT devices can also be used to alert authorities in emergency situations, ensuring a prompt response and ensuring the safety of students and staff.
5.4 Learning Analytics
The data generated by IoT devices in the classroom provide valuable insights through learning analytics. By analyzing data on student behavior, engagement, and performance, educators and administrators can identify patterns and trends. These insights can help in making data-driven decisions to improve teaching methods, curriculum design, and personalized interventions for students who may be struggling. Learning analytics also provide feedback to students, empowering them to self-reflect and enhance their learning strategies.
Online Learning Platforms and MOOCs
6.1 Flexibility and Accessibility
Online learning platforms and Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) have revolutionized the way education is delivered. These platforms offer flexible learning options, allowing students to study at their own pace and time preferences. Online learning eliminates geographical barriers, enabling students to access high-quality education from top institutions around the globe. Whether it’s a full degree program or short, skill-specific courses, online learning platforms provide opportunities for lifelong learning and professional development.
6.2 Global Learning Communities
Online learning platforms and MOOCs foster global learning communities where students from diverse backgrounds can connect and collaborate. Through discussion forums, virtual study groups, and peer-to-peer interactions, students can engage with peers from different cultures and perspectives. This global connection enhances cross-cultural understanding, strengthens communication skills, and promotes collaborative problem-solving.
6.3 Lifelong Learning Opportunities
Online learning platforms and MOOCs have democratized education by providing access to a wide range of courses and resources. Learners of all ages and backgrounds can engage in lifelong learning, acquiring new skills and knowledge to adapt to the rapidly evolving job market. Online learning platforms offer specialized courses in emerging fields, enabling professionals to upskill or reskill, ensuring their continued professional growth and competitiveness.
6.4 Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs)
MOOCs have gained significant popularity in recent years due to their scalability and accessibility. These courses are offered by prestigious institutions and cover a wide range of subjects. MOOCs provide interactive video lectures, quizzes, assignments, and discussion forums, creating a structured learning experience. Learners can earn certificates upon completion, enhancing their credentials and demonstrating their commitment to continuous learning.
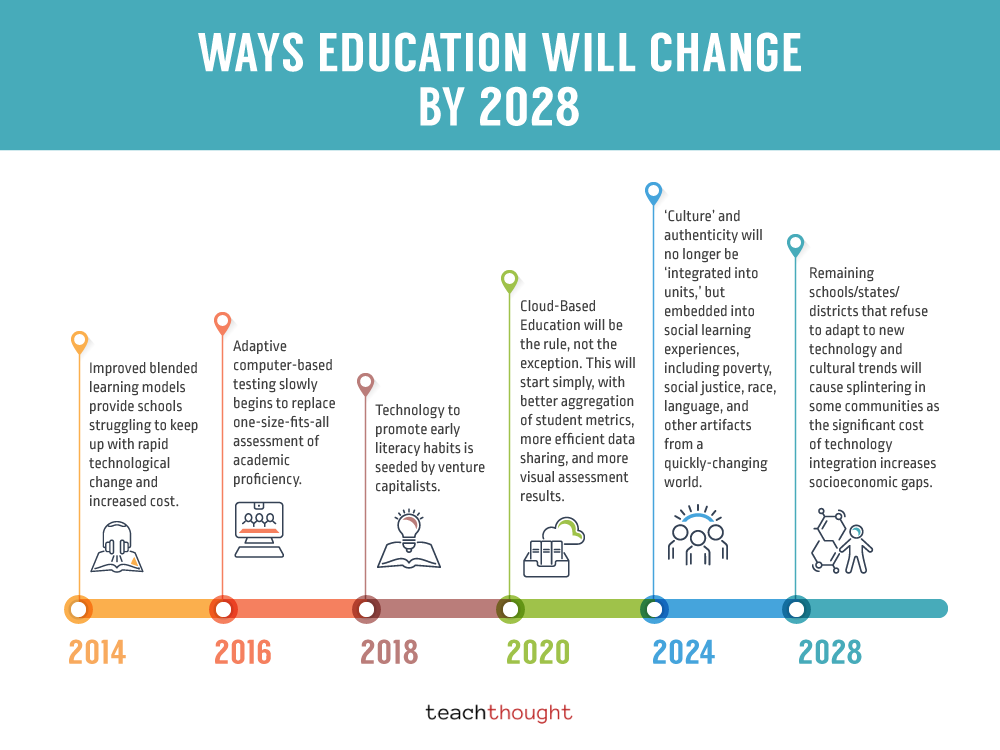
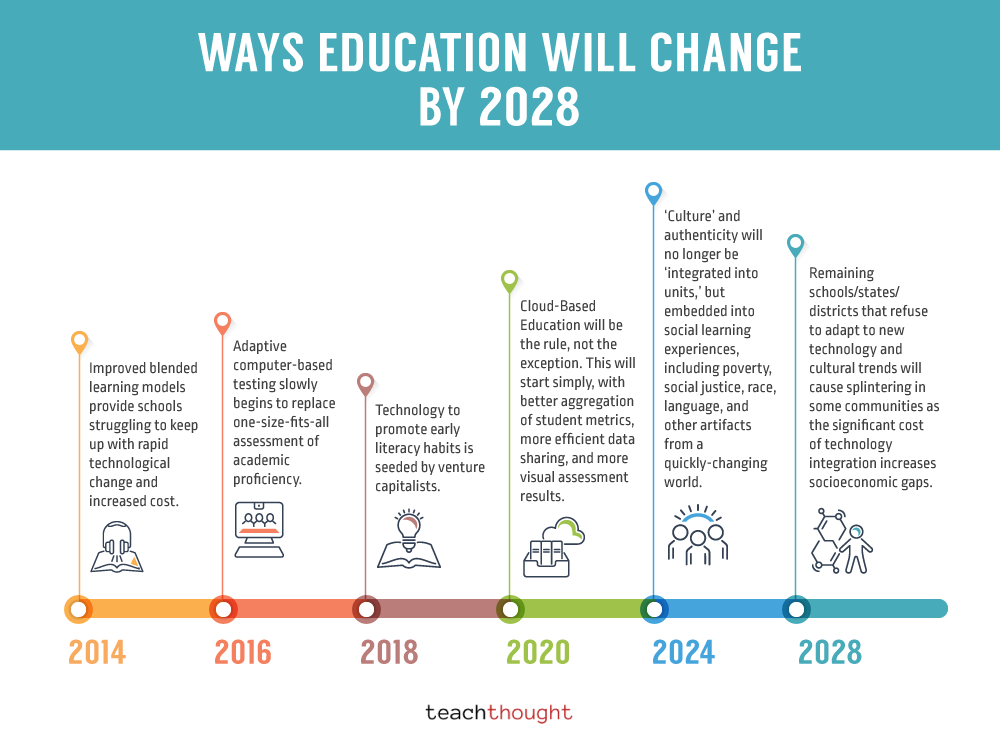
This image is property of www.teachthought.com.
Blended Learning Approaches
7.1 Combination of Online and Offline Instruction
Blended learning combines online and offline instruction to create a comprehensive learning experience. In a blended learning environment, students have the flexibility to access content and resources online, while also benefitting from face-to-face interactions with teachers and peers in the classroom. This approach optimizes the advantages of both online and offline instruction, allowing students to engage in collaborative activities, hands-on projects, and personalized instruction.
7.2 Personalized Learning Paths
Blended learning allows for personalized learning paths, catering to individual student needs and preferences. By leveraging online platforms, students can navigate through content at their own pace, review materials, and engage in online assessments to self-assess their understanding. Teachers can then individualize instruction during classroom sessions, providing targeted support and addressing specific learning gaps. This personalized learning approach promotes student autonomy and ownership of their learning journeys.
7.3 Synchronous and Asynchronous Learning
Blended learning offers a combination of synchronous and asynchronous learning opportunities. Synchronous learning involves real-time interactions between teachers and students, either in the physical classroom or through virtual classrooms. Asynchronous learning, on the other hand, allows students to access and engage with course materials at their convenience. Blended learning provides a balance between real-time collaboration and self-paced learning, accommodating different learning styles and preferences.
7.4 Hybrid Classroom Models
Blended learning has paved the way for hybrid classroom models, where students alternate between physical classroom instruction and virtual learning. This model combines the benefits of face-to-face interactions and online resources. In hybrid classrooms, students can access instructional materials online, engage in collaborative activities, and participate in virtual discussions. They also have the opportunity for in-person interactions with teachers and peers, fostering social and emotional development.
Blockchain Technology in Education
8.1 Secure and Verifiable Credentials
Blockchain technology offers secure and verifiable credentials in education. By storing educational records on a tamper-proof and decentralized blockchain ledger, credentials such as degrees, certificates, and diplomas can be securely issued and verified. This eliminates the risk of fraudulent credentials and provides students with a secure way to authenticate their qualifications. Blockchain technology also simplifies the process of credential verification for employers and educational institutions, reducing administrative burdens and ensuring the integrity of academic achievements.
8.2 Transparent and Tamper-proof Record-keeping
Blockchain technology ensures transparent and tamper-proof record-keeping in education. All transactions and changes to educational records are stored in a distributed ledger, making them transparent and traceable. This transparency enhances the trust and integrity of educational systems, as records cannot be manipulated or tampered with. Educational institutions and employers can have confidence in the accuracy and authenticity of educational records, simplifying the verification process and minimizing the risk of forged or misrepresented qualifications.
8.3 Easier Transfer of Educational Records
Blockchain technology streamlines the transfer of educational records between institutions, making the process more efficient and secure. With the use of blockchain, students can securely share their educational records with other institutions or potential employers, ensuring a seamless transfer of information. This eliminates the need for manual record transfers, reducing administrative burdens and enabling faster decision-making in enrollment or hiring processes.
8.4 Streamlined Verification Processes
Blockchain technology simplifies the verification processes in education. Instead of going through time-consuming and often manual verification procedures, educational institutions and employers can easily verify the authenticity of credentials by accessing the blockchain records. This streamlines the verification process, saving time and reducing administrative costs. The use of blockchain technology ensures a more reliable and efficient verification system, benefitting both students and institutions.

This image is property of s3-us-east-2.amazonaws.com.
Data Analytics and Learning Analytics
9.1 Data-driven Decision-making
Data analytics in education enables data-driven decision-making, empowering educators and administrators to make informed choices. By collecting and analyzing data on student performance, engagement, and behavior, educators can gain insights into teaching effectiveness, curriculum design, and resource allocation. Data analytics can identify trends and patterns that can inform instructional strategies and personalized interventions to optimize student learning outcomes.
9.2 Personalized Recommendations and Interventions
Learning analytics leverage data to provide personalized recommendations and interventions for students. By analyzing individual student data, learning analytics systems can identify areas of improvement, recommend resources, and offer personalized learning paths. This personalized approach ensures that students receive the support and resources they need to succeed, increasing their engagement and academic performance.
9.3 Predictive Analytics for Student Success
Predictive analytics in education use historical data to predict student outcomes and identify students who may be at risk of academic challenges or dropouts. By analyzing factors such as attendance, engagement, and performance data, predictive analytics models can generate early warning indicators and alert educators to provide targeted support. This proactive intervention can mitigate potential issues and enhance student success rates.
9.4 Continuous Improvement of Teaching Methods
Data analytics and learning analytics support the continuous improvement of teaching methods. By analyzing student data, educators can identify areas where their teaching methods may need adjustment or improvement. This feedback loop allows educators to refine their instructional strategies, delivery methods, and assessments to better meet the needs of their students. Continuous improvement of teaching methods enhances student learning experiences and fosters a culture of innovation in education.
Cybersecurity in Education
10.1 Protecting Student and Teacher Data
Cybersecurity in education is essential to protect sensitive student and teacher data. Educational institutions handle large amounts of personal and confidential information, including academic records, financial data, and personally identifiable information. By implementing robust cybersecurity measures, such as firewalls, encryption, and secure access controls, institutions can safeguard this data from unauthorized access, data breaches, and identity theft. Protecting student and teacher data promotes trust and maintains the integrity of educational systems.
10.2 Safeguarding Digital Infrastructure
Educational institutions rely heavily on digital infrastructure, such as networks, servers, and cloud-based platforms, to deliver education effectively. Cybersecurity measures are essential to safeguard this digital infrastructure from cyber threats such as malware, ransomware, and unauthorized access. By implementing cybersecurity protocols, regular vulnerability assessments, and staff training, institutions can ensure the resilience and reliability of their digital systems.
10.3 Promoting Responsible Digital Citizenship
Cybersecurity in education also involves promoting responsible digital citizenship among students. Educators play a crucial role in educating students about online safety, privacy, and responsible use of technology. By teaching students about the risks and ethical considerations associated with digital technologies, educators empower them to make informed decisions and behave responsibly in the digital world. Promoting responsible digital citizenship creates a safer online environment for students and helps them develop lifelong skills in digital literacy and responsible technology use.
10.4 Training for Cybersecurity Awareness
Educators and staff should receive training in cybersecurity awareness to mitigate risks and protect educational systems. Training programs can provide guidance on recognizing phishing attempts, using strong passwords, protecting personal information, and detecting potential security vulnerabilities. By equipping educators with cybersecurity knowledge and best practices, institutions can create a culture of cybersecurity awareness and resilience.
In conclusion, technological innovation has had a profound impact on education, enhancing access, personalization, collaboration, resources, and several other aspects of the learning experience. Integrating artificial intelligence, utilizing gamification, leveraging virtual and augmented reality, adopting IoT, embracing online learning platforms and MOOCs, implementing blended learning approaches, exploring blockchain technology, harnessing data analytics, and prioritizing cybersecurity are just a few of the innovative approaches shaping the future of education. As technology continues to evolve, it is essential for educators and institutions to embrace these advancements to ensure that education remains relevant, engaging, and accessible in the digital age.

This image is property of bmmagazine.co.uk.